A motor comparison: STEP versus PCBMotor
-
Stepper Motor – A conventional electromagnetic motor
Using built-in step motor functionality for position control, stepper motors can divide a full rotation off 200 steps into 256 microsteps per full step totaling a maximum of 51,200 microsteps.
Stepper motors are ‘constant power’ devices that use open-loop motion control and don’t include feedback to determine whether or not the desired position has been achieved.
The common phenomenon that stepper motors occasionally lose steps – which can cause adverse effects within an application – force engineers and designers to compensate by choosing a larger and more powerfull motor, to overcome this.
The ‘constant power’ requirement of stepper motors to maintain position, will have a detrimental impact on power-critical positioning applications.
-
PCBMotor – A patented, cutting-edge piezo innovation
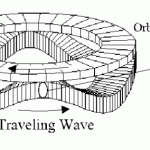
A PCBMotor is the latest development in rotational, piezoelectric motor technology that provides movement in applications without any slack or play.
As the basic elements in a PCBMotor are surface mounted devices (SMD), it’s very cost effective to implement a position sensor with the desired precision – where each position can divide a full rotation into a maximum 2.6 million resolutions (0.5 arc seconds) using micro-pulsing.
PCBMotors operate in open-loop mode and can deploy any kind of position sensor to define the required precision of the code wheel to achieve the desired position and velocity using closed-loop motion control with feedback control system.
Tell your project team
PCBMotor technology utilizes
- Standard electronic industry (volume) production methods
- Piezo ceramics mounted as SMD components
- State-of-the-art, “pick & place” assembly techniques that mounts in seconds
- ”Landing bridges” to connect the stator to the driver
To use a PCBMotor if you need to 
- Lower bill of materials, production costs
- Reduce application size (height, weight, space)
- Promote innovative designs
- Maintain full holding torque in power-off mode
A comparison: Judge for yourself
The table below highlights and describes the major differences between these two motor technologies – step motors and PCBMotors.
It’s aimed at giving project managers, application designers and engineers a reference point upon which to base – and justify – their final choice of motor.
Prev Chapter 1 – Gains